India-USA Trade Deal:Tensions between India and the United States have escalated after President Donald Trump imposed a 25% tariff on Indian goods starting August 7, 2025, along with a penalty over India’s trade with Russia. Despite pressure from Washington, India has firmly refused to open its agriculture and dairy sectors to U.S. products, citing protection of farmers and small enterprises. The sixth round of trade talks is scheduled for August 25 in New Delhi, with hopes of reaching an interim deal. Meanwhile, India is preparing retaliatory measures under WTO rules and exploring alternate trade partners.
India-USA Trade Deal:Tariffs Imposed by the United States
On August 1, 2025, President Donald Trump signed an executive order announcing a steep 25% tariff on a wide range of Indian goods. These tariffs are set to come into effect from August 7, 2025. In addition to these duties, the executive order also includes an unspecified “penalty” against India for continuing trade relations with Russia, particularly focusing on India’s ongoing purchases of Russian crude oil.
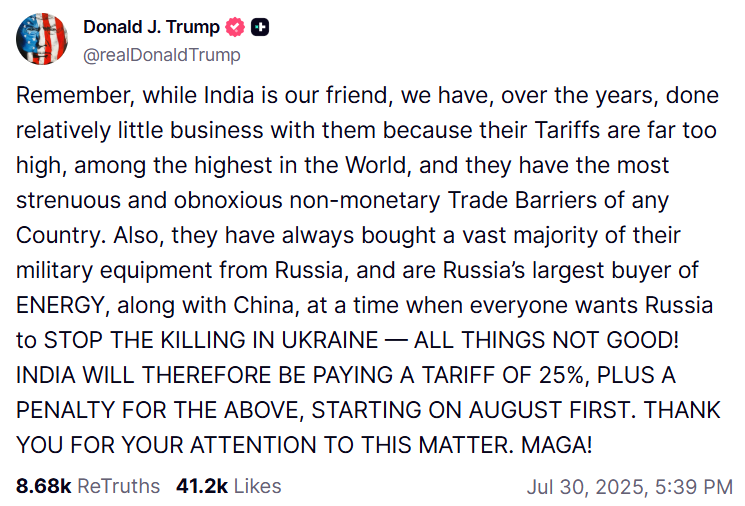
The White House has framed these tariffs as a pressure tactic to accelerate progress toward a comprehensive trade deal with India. The administration believes that India has been dragging its feet in opening up critical sectors for US access, and this move is designed to extract greater concessions from New Delhi. However, this aggressive approach has only deepened the stalemate in the trade talks, sparking concern among policymakers and industry players on both sides.
India-USA Trade Deal:India’s Unyielding Position on Agriculture and Dairy
One of the key sticking points in the negotiations remains India’s unwillingness to open its agricultural and dairy markets to American goods. These sectors are not only economically crucial but also politically sensitive. India’s agricultural and dairy industries support millions of small farmers and micro-enterprises, forming the backbone of rural employment and food security.
India has categorically stated that it will not allow genetically modified crops or foreign dairy products to flood its markets at the expense of local producers. Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal reiterated that protecting national interests, particularly the livelihood of farmers and small businesses, remains a non-negotiable aspect of any trade agreement.
Indian negotiators have emphasized that any deal undermining the country’s food sovereignty and rural economy will be unacceptable, even at the cost of delaying or derailing the trade pact. This firm stance has not gone down well with US trade officials, who view India’s agricultural policies as overly protectionist.
India-USA Trade Deal:Ongoing Negotiations: A Delicate Balancing Act
Despite the imposition of tariffs and widening disagreements, both sides are still at the negotiating table. The sixth round of trade talks is scheduled for August 25, 2025, when a US delegation will visit New Delhi to resume discussions. The focus will be on finalizing an interim trade deal, which could pave the way for a more comprehensive agreement in the future.
Indian officials remain cautiously optimistic that a breakthrough is possible by September or October 2025. However, negotiators acknowledge that unless the US revises its demands on agriculture and India shows some flexibility on market access for American goods, the talks could remain gridlocked.
Observers believe that even a limited agreement covering sectors like digital trade, services, and manufacturing standards could be a stepping stone to more ambitious goals. Still, both sides need to demonstrate political will and strategic vision to overcome the current deadlock.
India-USA Trade Deal:India’s Response to US Tariffs
India has not taken the new tariffs lightly. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry is currently analyzing the scope and impact of the 25% duties. Government officials have indicated that India reserves the right to respond under World Trade Organization (WTO) rules, including imposing retaliatory tariffs on US goods if necessary.
Furthermore, India is exploring ways to minimize its dependence on any single trading partner. This includes diversifying trade partnerships and increasing exports to the EU, UK, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The government is also reportedly working on enhancing incentives for exporters and boosting competitiveness in labor-intensive sectors.
While New Delhi has not yet officially announced countermeasures, trade experts believe that India could target American agricultural products, liquefied natural gas (LNG), and Harley-Davidson motorcycles, which have been symbolic flashpoints in the past.
India-USA Trade Deal:Economic Stakes: What the Numbers Say
The economic implications of the new tariffs are significant. Bilateral trade between India and the United States stood at around $130 billion in 2024, making the US one of India’s largest trading partners. Key Indian exports to the US include smartphones, pharmaceuticals, textiles, gems and jewelry, seafood, and industrial equipment.
The 25% tariff is expected to particularly hurt labor-intensive sectors such as jewelry, textiles, and seafood, potentially leading to job losses in export-oriented clusters across Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. However, early indications suggest that high-value exports like smartphones and pharmaceutical drugs may receive exemptions, thereby softening the overall blow to India’s trade earnings.
At the same time, Indian IT and services exports, which account for a significant chunk of bilateral trade, remain unaffected by the new tariffs. This sector could act as a stabilizing force amid the uncertainty surrounding goods trade.
India-USA Trade Deal:Strategic Calculations and Geopolitical Leverage
Beyond economic considerations, strategic factors are shaping the contours of the India-US trade dialogue. The United States views India as a vital counterbalance to China’s growing influence in the Indo-Pacific. In this context, maintaining strong economic ties with New Delhi serves broader geopolitical interests for Washington.
Analysts point out that an excessively confrontational approach risks pushing India closer to other global powers, such as Russia and China, undermining US strategic goals in the region. India, for its part, continues to pursue a policy of multi-alignment, actively engaging with multiple economic and strategic partners.
New Delhi is already negotiating or finalizing trade deals with the European Union, the United Kingdom, and regional powers like the Maldives. These ongoing negotiations give India leverage, reducing its dependence on any one country and allowing it to play a more assertive role in global trade discussions.
India-USA Trade Deal: The Road Ahead
India-USA Trade Deal:As the countdown begins for the sixth round of India-US trade negotiations, the stakes couldn’t be higher. The new US tariffs have undoubtedly added urgency to the talks, but they have also deepened existing fault lines. For a mutually beneficial deal to materialize, both nations will have to strike a fine balance between economic interests and strategic imperatives on India-USA Trade Deal
India-USA Trade Deal:India’s emphasis on protecting its agricultural base and strategic autonomy stands in contrast to the US demand for greater market access. However, with global trade patterns shifting and geopolitical alliances evolving, both countries have strong incentives to find common ground. Whether the upcoming negotiations produce a meaningful breakthrough or more diplomatic friction remains to be seen—but one thing is certain: the world will be watching on India-USA Trade Deal

